How Many Grams Of Protein Are In Two Large Eggs
eviana
Dec 03, 2025 · 9 min read
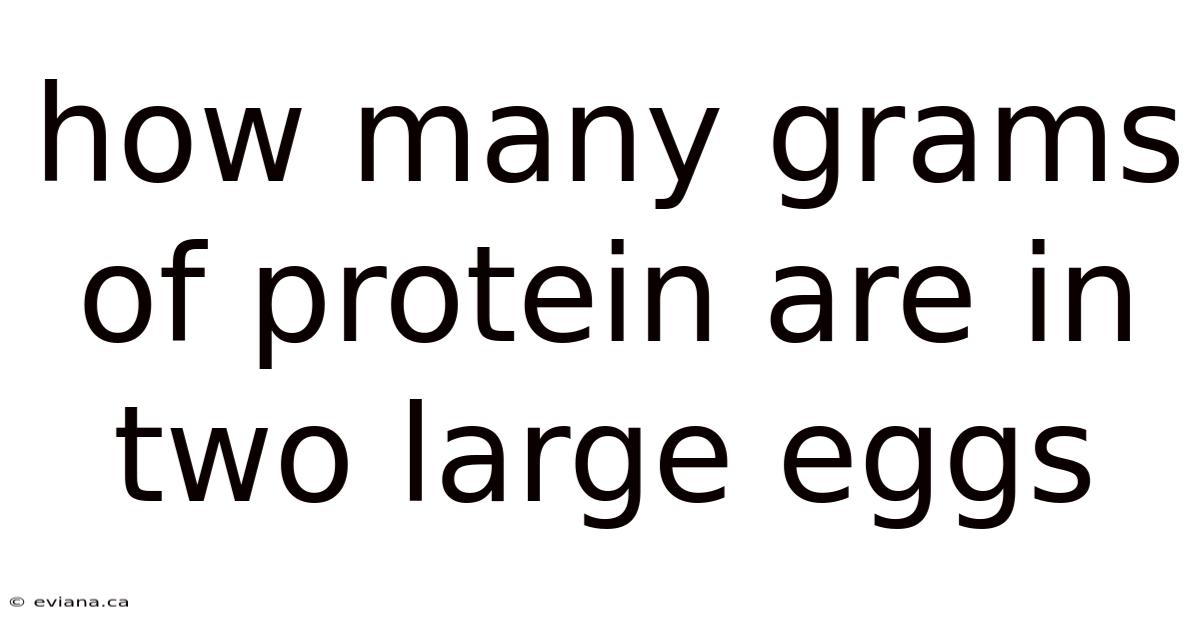
Table of Contents
Imagine starting your day with a simple yet powerful breakfast: two large eggs, sunnyside up, nestled beside a slice of whole-wheat toast. Beyond their satisfying taste and visual appeal, these eggs pack a nutritional punch, most notably a significant dose of protein. But have you ever stopped to consider exactly how many grams of protein are in two large eggs?
For fitness enthusiasts, health-conscious individuals, and anyone curious about their daily protein intake, understanding the protein content of common foods like eggs is essential. Protein is a macronutrient vital for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily function. Let's crack open the facts about eggs and explore their protein contribution to your diet.
The Protein Power of Eggs: A Detailed Breakdown
To answer the question directly, two large eggs contain approximately 12-14 grams of protein. This makes them a readily accessible and efficient source of high-quality protein. However, understanding the nuances of this number—where the protein is located within the egg and how it benefits your body—is key to appreciating the full value of this breakfast staple.
Comprehensive Overview of Egg Protein
Defining Protein
Protein is one of the three macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and fats, that our bodies need to function properly. It's composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our tissues and cells. Protein plays a critical role in:
- Muscle Building and Repair: Protein is essential for repairing muscle tissue after exercise and building new muscle mass.
- Enzyme Production: Enzymes, which catalyze countless biochemical reactions in the body, are made of protein.
- Hormone Synthesis: Many hormones, which regulate various bodily functions, are also protein-based.
- Immune Function: Antibodies, which help fight off infections, are proteins.
- Transportation: Proteins transport molecules throughout the body, such as oxygen via hemoglobin.
The Protein Composition of an Egg
A single large egg weighs around 50 grams and contains approximately 6-7 grams of protein. This protein is distributed between the egg white (albumen) and the egg yolk.
- Egg White: The egg white comprises about 60% of the egg's total protein. It's almost pure protein, with minimal fat. The primary protein in egg white is ovalbumin, which makes up more than half of the total protein content. Other proteins present in the egg white include conalbumin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme.
- Egg Yolk: The egg yolk contains the remaining 40% of the protein, along with essential fats, vitamins, and minerals. The proteins in the yolk are more complex, including lipoproteins (proteins bound to fats) such as lipovitellin and lipoprotein.
Biological Value of Egg Protein
Egg protein is considered a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot synthesize on its own. These essential amino acids must be obtained from the diet. The quality of a protein is often measured by its biological value (BV), which assesses how efficiently the body can use the protein. Egg protein has one of the highest biological values, often rated around 100, indicating that the body can efficiently absorb and utilize its amino acids.
The Nutritional Benefits Beyond Protein
While protein is a key highlight, eggs offer a spectrum of other nutritional benefits:
- Vitamins: Eggs are rich in vitamins such as vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and several B vitamins, including vitamin B12 and folate.
- Minerals: They provide essential minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium.
- Healthy Fats: The yolk contains healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health and brain function.
- Choline: Eggs are an excellent source of choline, an essential nutrient crucial for brain health and cell membrane structure.
- Antioxidants: Eggs contain antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for eye health and may reduce the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
Historical Significance of Eggs in Human Diets
Eggs have been a staple in human diets for millennia. Domesticated chickens, the primary source of eggs today, are believed to have originated in Southeast Asia. Eggs have been valued for their nutritional content and versatility across various cultures.
- Ancient Civilizations: Evidence suggests that humans consumed eggs as far back as ancient Egypt and Rome. They were often depicted in art and used in religious ceremonies.
- Traditional Medicine: In traditional medicine systems, eggs were used to treat various ailments, from skin conditions to digestive issues.
- Culinary Staple: Throughout history, eggs have been a fundamental ingredient in countless dishes, from simple omelets to elaborate pastries.
Trends and Latest Developments in Egg Consumption
In recent years, there's been a resurgence in the popularity of eggs, driven by a growing understanding of their nutritional benefits and a shift away from outdated dietary advice.
- Debunking Cholesterol Myths: For many years, eggs were unfairly demonized due to their cholesterol content. However, research has shown that dietary cholesterol has a minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels for most people. The saturated and trans fats in the diet have a more significant impact on blood cholesterol.
- Rise in Egg Consumption: As cholesterol concerns have eased, egg consumption has steadily increased. Eggs are now recognized as a healthy and affordable protein source.
- Variations in Egg Types: Consumers have more choices than ever when it comes to eggs. Options include:
- Cage-Free Eggs: Laid by hens that are not confined to cages.
- Free-Range Eggs: Laid by hens that have access to outdoor areas.
- Organic Eggs: Laid by hens that are fed organic feed and are not treated with antibiotics or hormones.
- Omega-3 Enriched Eggs: Laid by hens fed a diet supplemented with omega-3 fatty acids.
- Egg-Based Products: The market for egg-based products is expanding, with items like liquid egg whites, egg protein powders, and ready-to-eat egg snacks becoming increasingly popular.
Tips and Expert Advice for Incorporating Eggs into Your Diet
Eggs are incredibly versatile and can be incorporated into your diet in numerous ways. Here are some practical tips and expert advice:
-
Start Your Day Right: As mentioned earlier, eggs are an excellent breakfast option. They provide a sustained release of energy and help keep you feeling full and satisfied, which can prevent overeating later in the day. Try scrambled eggs with vegetables, a frittata, or a simple omelet.
Adding vegetables like spinach, mushrooms, or bell peppers not only enhances the flavor but also boosts the nutritional content of your meal. Experiment with different herbs and spices to add variety. A dash of turmeric can add anti-inflammatory benefits, while a sprinkle of chili flakes can provide a metabolic kick.
-
Use Eggs in Baking: Eggs are essential ingredients in many baked goods, providing structure, moisture, and richness. They help bind ingredients together and contribute to the texture of cakes, cookies, and muffins.
When baking, consider using pasteurized eggs if you're concerned about Salmonella. Also, be mindful of the fat content in the yolks and adjust other fat sources in the recipe accordingly. For a lighter option, you can use egg whites instead of whole eggs in some recipes.
-
Add Eggs to Salads and Bowls: Hard-boiled eggs are a fantastic addition to salads and grain bowls. They add protein and healthy fats, making the meal more satisfying and nutritionally complete.
Prepare a batch of hard-boiled eggs at the beginning of the week for easy meal prep. Store them in the refrigerator and add them to salads, sandwiches, or as a quick snack. Experiment with different seasonings, such as paprika, everything bagel seasoning, or a sprinkle of sea salt.
-
Make Deviled Eggs: Deviled eggs are a classic appetizer that's both delicious and nutritious. They're easy to make and can be customized with different flavors and toppings.
Try adding avocado for creaminess, Dijon mustard for tanginess, or a sprinkle of smoked paprika for a smoky flavor. Garnish with fresh herbs like chives or dill for a pop of color and freshness.
-
Explore Egg-Based Sauces: Eggs can be used to create rich and creamy sauces like hollandaise and aioli. These sauces can elevate simple dishes and add a touch of elegance to your meals.
When making egg-based sauces, it's important to use fresh, high-quality eggs and follow the recipe carefully to avoid curdling. Use a double boiler or a low heat setting to gently cook the eggs and prevent them from overheating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are all eggs the same in terms of protein content?
A: While the protein content is relatively consistent, slight variations can occur based on the size of the egg and the breed of the hen. Larger eggs will naturally contain slightly more protein than smaller eggs.
Q: Is it better to eat the whole egg or just the egg white for protein?
A: Eating the whole egg is generally recommended. While the egg white is a pure protein source, the yolk contains essential nutrients, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
Q: Can eating too many eggs be bad for you?
A: For most people, eating eggs in moderation (up to one or two per day) is not harmful and can be part of a healthy diet. Individuals with specific health conditions, such as high cholesterol or diabetes, should consult with their healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Q: How should eggs be stored to maintain their quality and freshness?
A: Eggs should be stored in the refrigerator at a consistent temperature. Keep them in their original carton to prevent them from absorbing odors and flavors from other foods.
Q: What's the best way to cook eggs to preserve their nutritional value?
A: Eggs can be cooked in various ways, including boiling, frying, scrambling, poaching, and baking. The cooking method has minimal impact on the protein content, but it can affect the availability of certain vitamins. Overcooking eggs can reduce the availability of some nutrients, so it's best to cook them until they are just set.
Conclusion
So, how many grams of protein are in two large eggs? The answer, around 12-14 grams, underscores the nutritional value of this simple food. Eggs are a complete protein source, packed with essential amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. Whether you're aiming to build muscle, maintain a healthy weight, or simply nourish your body, incorporating eggs into your diet is a smart choice.
Now that you're equipped with this knowledge, consider how you can best integrate eggs into your daily meals. Experiment with different recipes, explore various egg options, and enjoy the numerous health benefits they offer. Share this article with your friends and family to spread the word about the protein power of eggs, and leave a comment below sharing your favorite way to enjoy them!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Temp At Ohio State Game Today
Dec 03, 2025
-
What Did Mark Anthony Look Like
Dec 03, 2025
-
Is Skinny Jeans Still In Style
Dec 03, 2025
-
How To Start A Screen Recording On Iphone
Dec 03, 2025
-
Best Wired Headsets For Working From Home
Dec 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Grams Of Protein Are In Two Large Eggs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.